Antiquarian Bible Identification: The Who, What, and Where
Antique Bible identification is an intriguing pursuit that melds passion for literature with the appreciation of history. This process involves discerning the unique attributes that distinguish various Bibles, often based on their age, condition, and cultural significance. To embark on this identification journey, it is crucial to recognize the defining aspects of antiquarian Bibles, which can vary greatly, leading to the discovery of valuable editions and insights into their provenance.

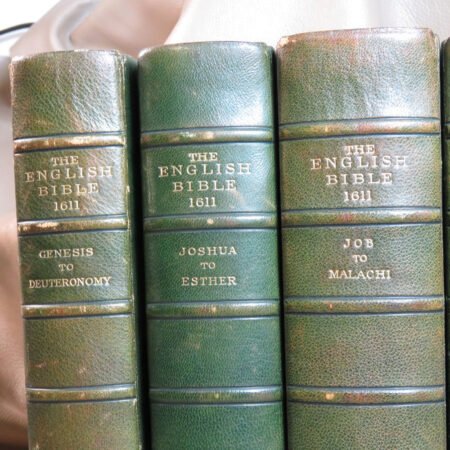
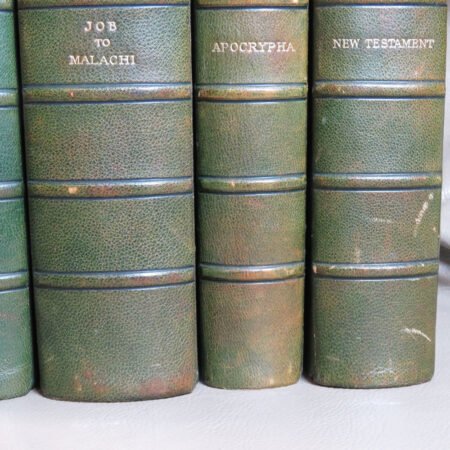
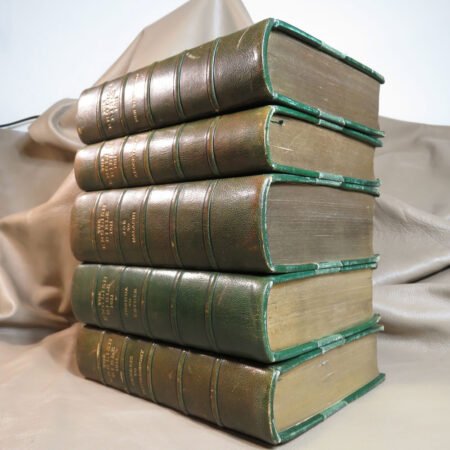
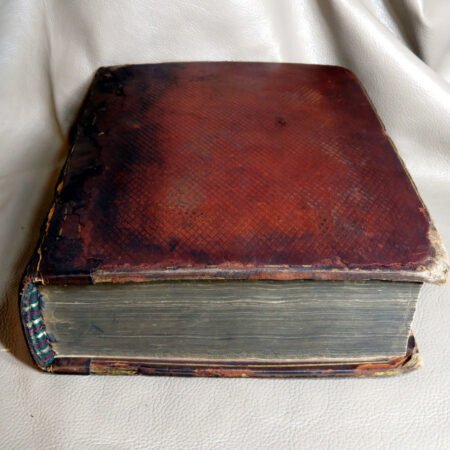
One of the primary factors to consider when identifying old Bibles is the age of the book. Generally, a Bible is considered antiquarian if it was produced before the 19th century. It is important to familiarize yourself with historical printing techniques and styles to accurately understand the timeline of the Bibles you encounter. Next, the condition of the book plays a vital role in its value and desirability. Pay attention to elements such as binding, paper quality, and any physical damage that may affect its integrity.
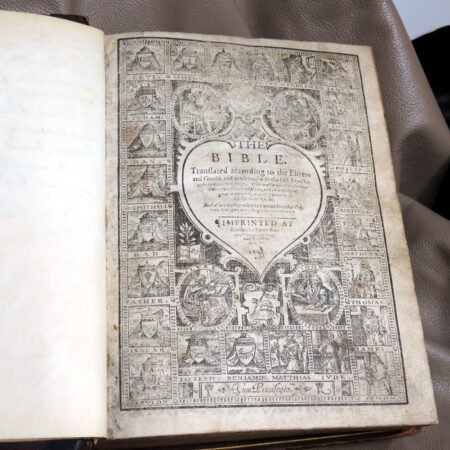
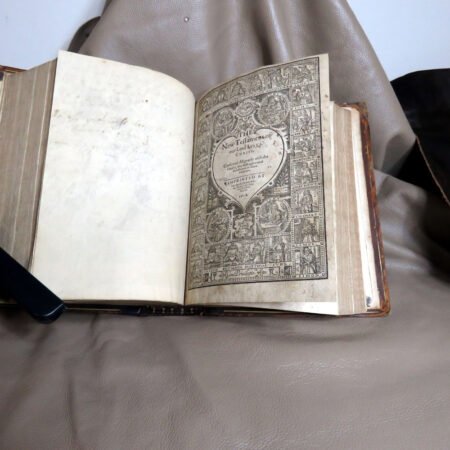
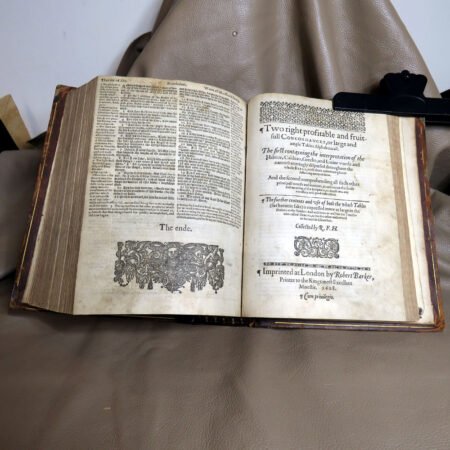
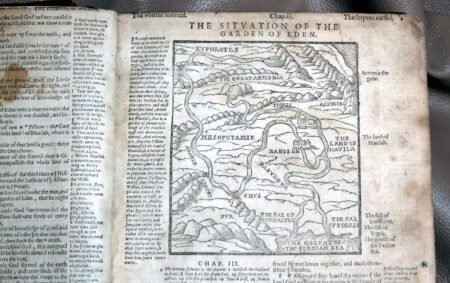
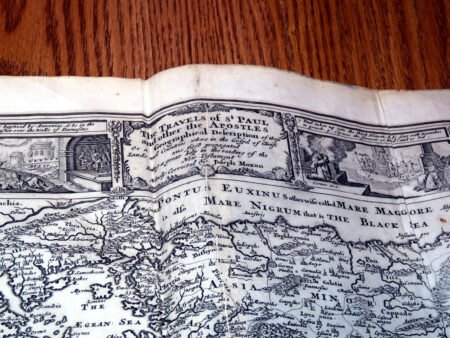
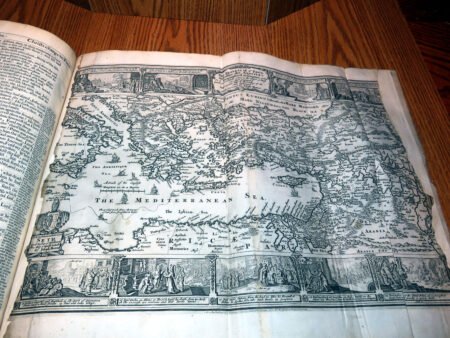
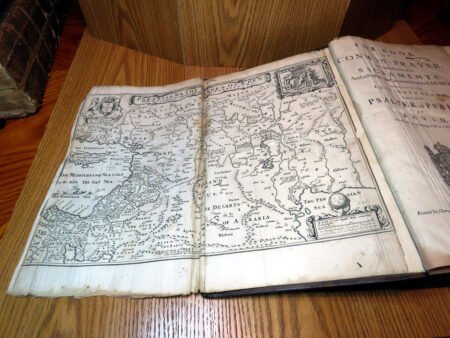
Additionally, bibliographic details are imperative for antique Bible authentication. Look for specifics such as printing dates, which reveal the era during which the Bible was produced. Publishers’ information can also shed light on the Bible’s origins and mean to collectors, while geographic details may provide insight into the regional context in which the Bible was published. Furthermore, familiarize yourself with various types of Bibles, such as family Bibles, pocket editions, and special illustrated copies, which can enhance your rare Bible editions guide.
As you delve deeper into the captivating realm of antique Bibles, remember that patience and keen observation are key. Engaging in this exploration equips you not only with knowledge but also with an appreciation for the history encapsulated within these sacred texts, ultimately enriching your ability to identify them accurately.
How to Identify Old Bibles: Spotting the Hidden Gems
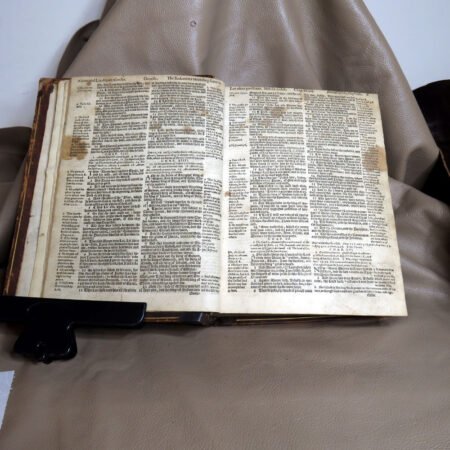
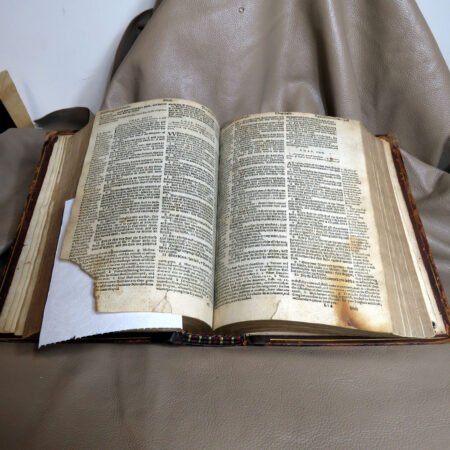
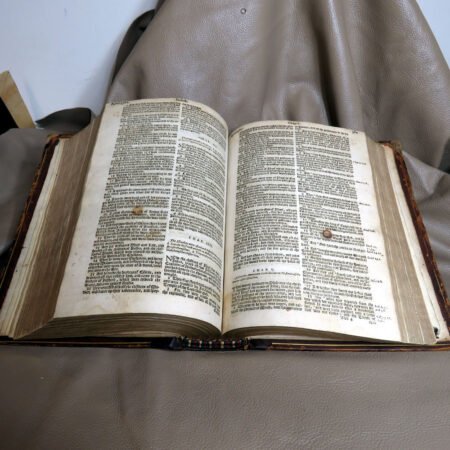
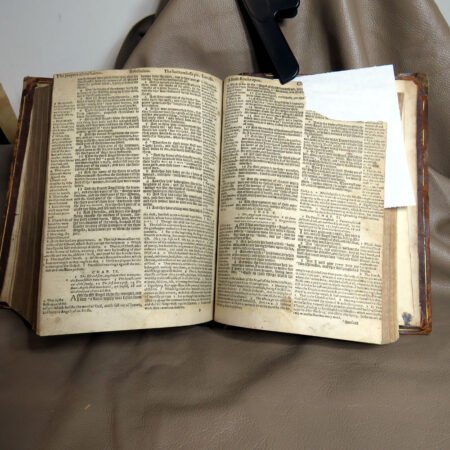
Identifying old Bibles requires a keen eye and an understanding of certain features that define their age. The process of antique bible identification can be fascinating, as each text tells a story through its physical attributes. One of the primary indicators is the type of paper used. Older Bibles often employed handmade rag paper, which has a distinct texture and weight compared to modern, machine-made paper. When examining a Bible, feel the pages; if they are soft and fibrous rather than smooth and sleek, you may have a vintage find.

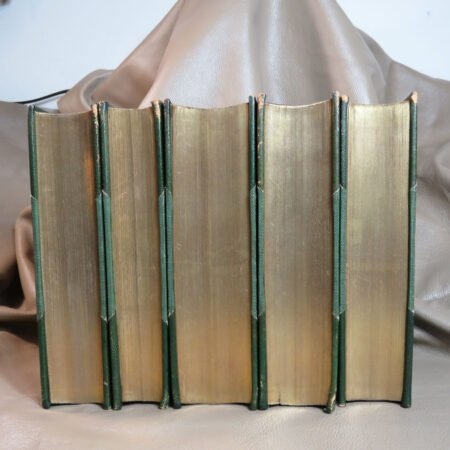
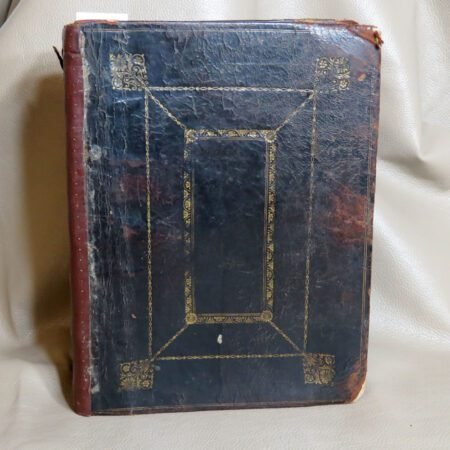
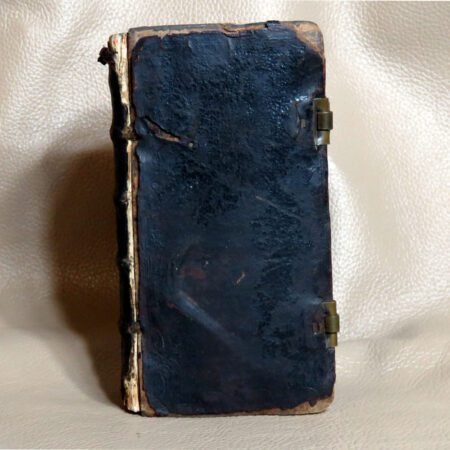
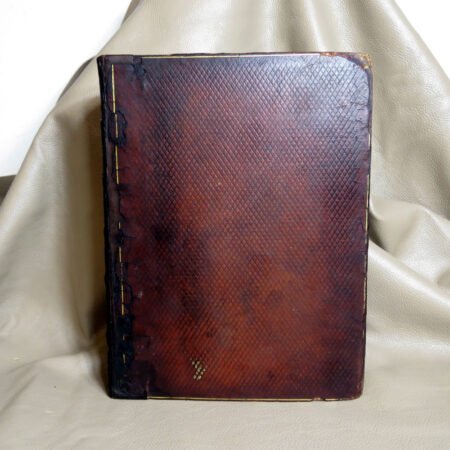
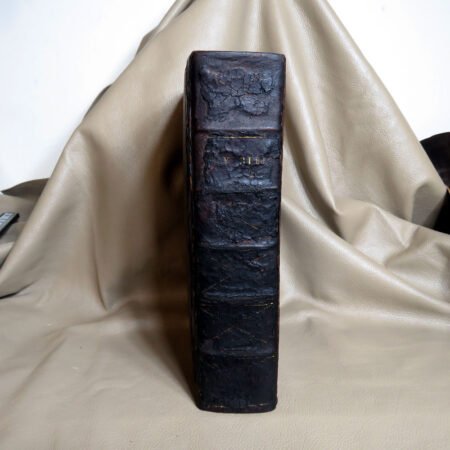
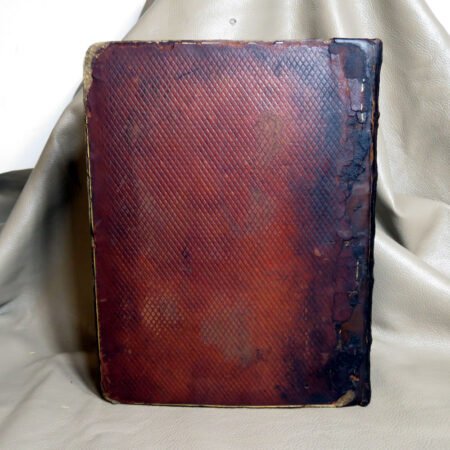
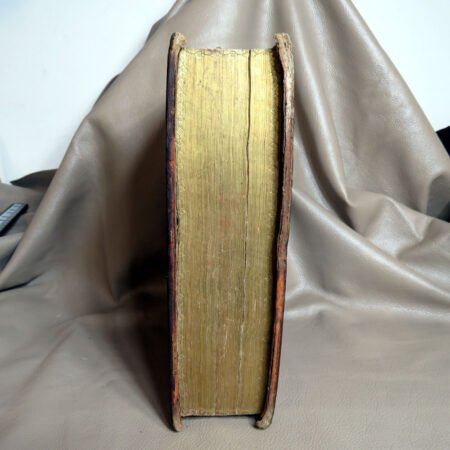
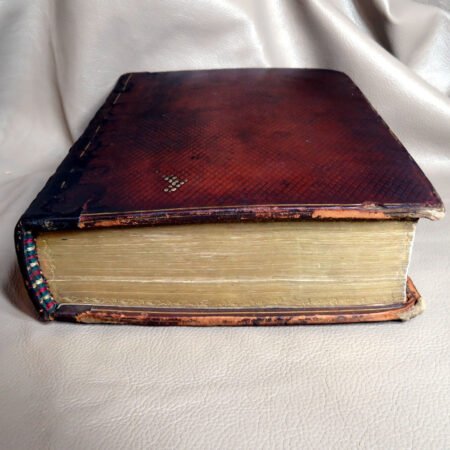
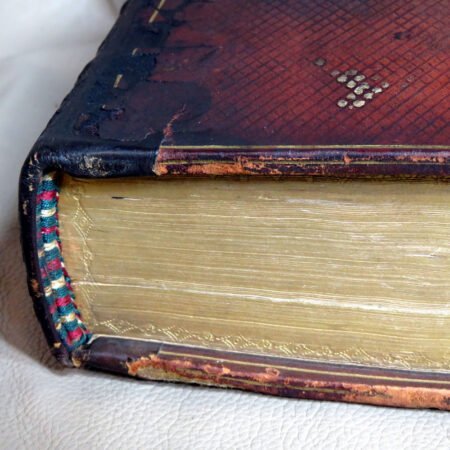
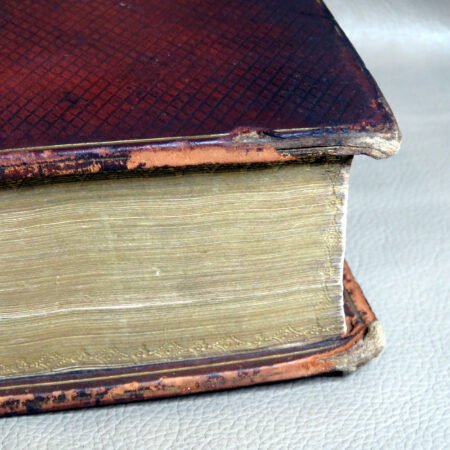
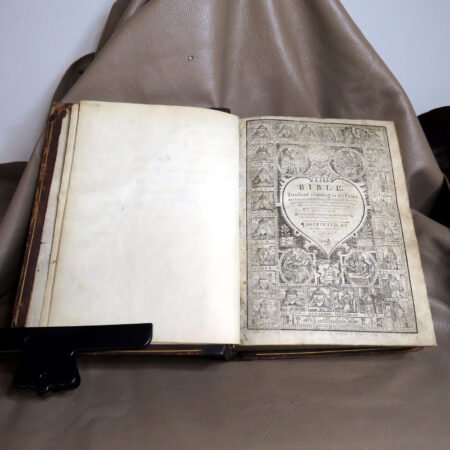
An important aspect of how to identify old Bibles lies in the binding style. Pre-20th century Bibles frequently utilized leather covers, and the quality of the leather—whether it is calfskin or goatskin—can further hint at its age. Pay attention to the binding method as well. Early editions were typically bound by hand, making their spines more fragile than those of contemporary books. Not to mention, the presence of gilded edges is another hallmark of antique Bibles.
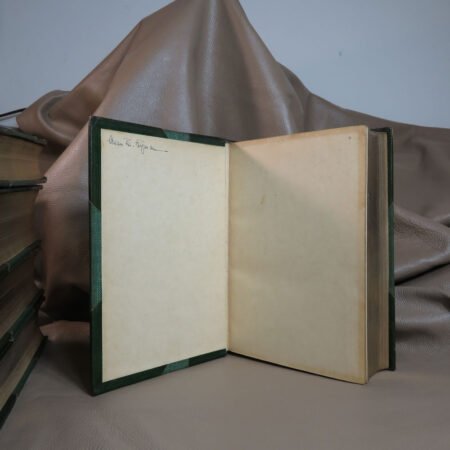
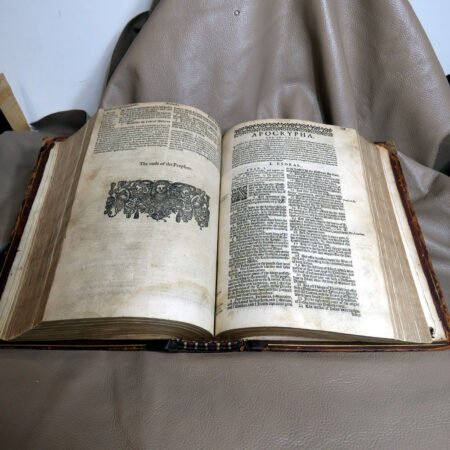
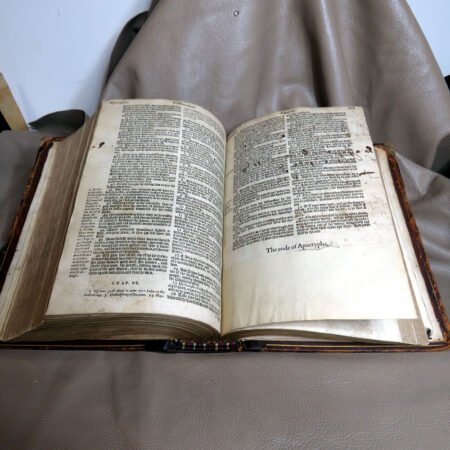
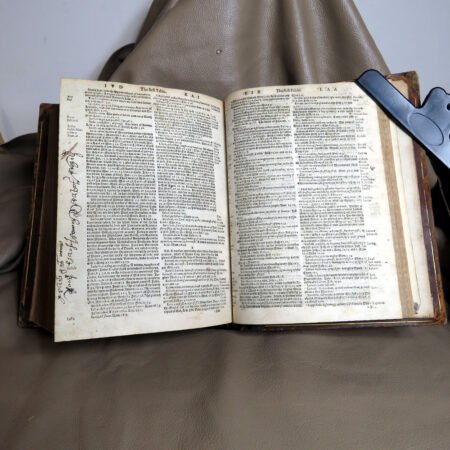
Illustrations and annotations also provide clues to dating antique Bibles. Old Bibles may contain engravings or unique illustrations that became less common in later publications. Some may even have handwritten notes or inscriptions within their pages that give insight into their history. Pairing anecdotal references, such as the humorous misidentifications encountered during assessments, can enhance the experience of exploration in antiquarian collections. Every misstep leads to a deeper appreciation of the quirks and tales that surround these old texts. Thus, taking the time to observe these details is crucial in mastering the art of antique bible authentication.
Authentication: Separating the Real from the Replica
Antique Bible authentication is a crucial step for collectors and historians seeking to verify the legitimacy of their prized possessions. With an increasing number of fakes and reproductions flooding the market, understanding how to identify old Bibles is essential. An effective strategy begins with thorough examination of provenance, which refers to the documented history of a Bible. In many cases, an original owner’s name, purchase receipts, or even handwritten notes can significantly help in tracing the authenticity of an antique Bible.

Furthermore, involving experts in antique bible authentication can elevate the verification process. Collectors are encouraged to collaborate with reputable appraisers and specialists in rare Bible editions, as they possess the experience and knowledge to assess historical accuracy. The process may involve examining binding materials, paper quality, typesetting, and even the watermark of the paper, which can often indicate the Bible’s age and legitimacy. Consulting with professionals helps bypass many pitfalls associated with misidentification and raises awareness regarding common myths that may mislead novice collectors.
As technology advances, modern methods such as archival analysis are becoming invaluable tools in the field. Techniques like infrared reflectography or X-ray fluorescence can uncover layers of text and reveal details hidden to the naked eye, providing further means to verify an antique Bible’s authenticity. However, it is vital to be cautious and consider the context—such advanced methods can sometimes produce ambiguous results that require seasoned judgment to interpret accurately.
To lighten the topic, consider the story of a collector who proudly displayed what they believed to be an original Gutenberg Bible, only to discover it was a clever replica, crafted just for the novelty market. Such humorous anecdotes serve as reminders that even the most seasoned collectors must remain vigilant in their pursuit of antique Bible authentication.
Rare Bible Editions Guide: What Makes a Bible Rare?
When it comes to antiquarian Bible identification, understanding what constitutes a rare edition is crucial for both collectors and enthusiasts alike. Several key factors contribute to a Bible’s rarity, with historical context playing a significant role. Certain editions may have been produced during pivotal moments in history, such as the Reformation or the American Revolutionary War, making them particularly sought after by collectors. For example, the Gutenberg Bible, printed in the 15th century, is one of the earliest major books printed using movable type, and its limited number of surviving copies has solidified its status as a treasure.
Beyond historical significance, unique textual variants often enhance a Bible’s value. Some Bibles include errors in printing or textual differences, which can increase their desirability. This is particularly true for editions like the “Wicked Bible,” which printed the commandment as “Thou shalt commit adultery,” leading to its recalls and rendering it extremely rare today. Collectors dedicated to antique Bible authentication will approach these editions with a discerning eye, verifying the authenticity of such misprints and understanding their implications.

In addition to textual and historical factors, the physical condition of a Bible plays an undeniable role in its rarity. Bibles that have been well preserved or exhibit unique bindings or illustrations often catch the eye of serious collectors. To find these rare editions, one should explore auctions, estate sales, and specialized antique shops, as these venues frequently hold hidden gems just waiting to be discovered. Connecting with other collectors may also provide valuable insights into notable rare editions and their tales. Each story adds to the rich tapestry of Bible history, illuminating how these ancient books have traveled through time and emerged as coveted artifacts in the modern world.
In conclusion, recognizing what makes a Bible rare involves understanding historical significance, unique textual variants, and physical condition. Armed with this knowledge, enthusiasts can embark on an exciting quest for rare Bibles, unlocking the pages of history in the process.